COCO annotations
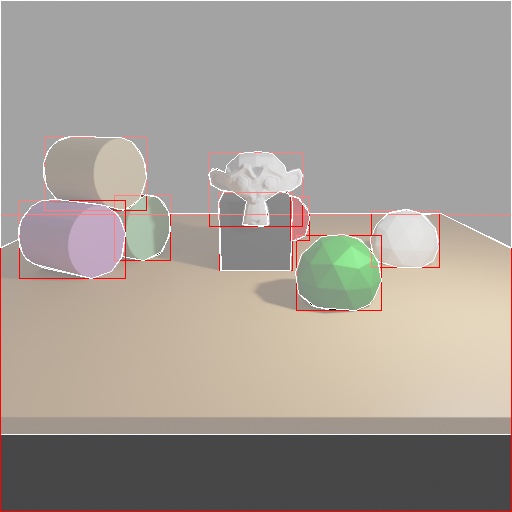
The focus of this example is to introduce user to writer.CocoAnnotationsWriter module.
Usage
Execute in the BlenderProc main directory:
blenderproc run examples/advanced/coco_annotations/main.py examples/resources/camera_positions examples/advanced/coco_annotations/scene.blend examples/advanced/coco_annotations/output
examples/advanced/coco_annotations/main.py: path to the main python file to run.examples/resources/camera_positions: text file with parameters of camera positions.examples/advanced/coco_annotations/scene.blend: path to the blend file with the basic scene.examples/advanced/coco_annotations/output: path to the output directory.
Visualizing Annotations
You can use vis coco_annotation.py with the following command to visualize the annotations blended over a rendered rgb image:
blenderproc vis coco [-i <image index>] [-c <coco annotations json>] [-b <base folder of coco json and image files>]
Working Examples
With specific values:
blenderproc vis coco -i 1 -c coco_annotations.json -b examples/advanced/coco_annotations/output/coco_data
Above are also the default values, i.e. for the same result call:
blenderproc vis coco
Implementation
# Set some category ids for loaded objects
for j, obj in enumerate(objs):
obj.set_cp("category_id", j+1)
# Render segmentation data and produce instance attribute maps
seg_data = bproc.renderer.render_segmap(map_by=["instance", "class", "name"])
To create coco annotations we need to render both instance and class maps. The class is defined in terms of a custom property category_id which must be previously defined for each instance. The category_id can be either set by a custom property as above or in a loader or can be directly defined in a .blend file.
We also add "name" to the mapping, s.t. we can later use the object’s names for labeling the categories in the coco annotations writer.
# Write data to coco file
bproc.writer.write_coco_annotations(os.path.join(args.output_dir, 'coco_data'),
instance_segmaps=seg_data["instance_segmaps"],
instance_attribute_maps=seg_data["instance_attribute_maps"],
colors=data["colors"],
color_file_format="JPEG")
This function stores annotations in coco_annotations.json. Optionally, you can set "supercategory": "<some_supercategory>" in the writer.CocoAnnotationsWriter config to filter objects by a previously assigned custom property "supercategory".